Hemorrhoids Online Registration
Because no single treatment modality can fix all hemorrhoids, a hemorrhoid clinic will offer multiple treatment modalities to meet a patient’s specific needs and provide complete care. If you are treated with a single modality, without regard for severity, type, and associated anorectal conditions (fissure, fistula, or warts), it can lead to poor and incomplete results.
Below are general treatment guidelines for various hemorrhoid diseases:
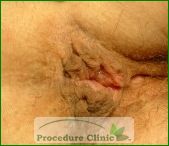
Internal Hemorrhoid, Grade 1
Very early-stage hemorrhoids can usually be treated via dietary and lifestyle changes, which form the base for all hemorrhoid treatment types:
Internal Hemorrhoid, Grade 1-2
The most common treatment method for hemorrhoids is infrared coagulation (IRC), a minimally-invasive, non-surgical procedure. A small probe is inserted into the anus to flash infrared light onto the surface of the hemorrhoid. The heat from this infrared probe burns the hemorrhoid and creates scar tissue that cuts off its blood supply, causing it to shrink and die. While patients may feel some heat and pain during the procedure, discomfort is usually brief and minimal. IRC is fast, well tolerated, and remarkably complication-free.
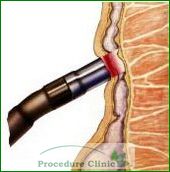 IRC offers major advantages over other hemorrhoid treatment methods:
IRC offers major advantages over other hemorrhoid treatment methods:
Internal Hemorrhoid, Grade 3
These can be treated with a combination of infrared coagulation and rubber band ligation (banding). Rubber band ligation is widely used for treating more advanced (more prolapsed) internal hemorrhoids where rubber bands are placed around the prolapsed hemorrhoidal tissue. Over time, the tissue dies off.
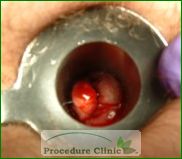
Internal Hemorrhoid, Grade 4
Grade 4 internal hemorrhoids are the most severe, with persistent prolapse of hemorrhoid tissue and often associated with external hemorrhoids. Surgical excision in the form of a hemorrhoidectomy is usually necessary. This procedure involves surgically removing the tissue that causes bleeding or protrusion. It is done in a doctor’s office, surgical center or hospital under anesthesia and may require a period of inactivity.
The alternative to a hemorrhoidectomy is PPH (Procedure for Prolapse and Hemorrhoids), otherwise known as a stapled hemorrhoidectomy. This procedure removes the loose tissue above the anus.
External Hemorrhoidal Tags (Anal Tags)
Small and asymptomatic tags don’t require any treatment. If symptomatic, anal tags can easily be removed in the office using a local anesthetic and a radiofrequency device.
Thrombosed External Hemorrhoids
These are typically treated with either incision to remove the clot or with an external hemorrhoidectomy. Simply draining the clot temporarily relieves the pain but can also lead to hemorrhoid recurrence, so it’s ideal for patients with multiple thromboses to completely excise the thrombosed hemorrhoids.
External Hemorrhoids
Small and asymptomatic external hemorrhoids don’t require any treatment, although most patients experience intermittent flare-ups. Surgery (external hemorrhoidectomy) may be needed in the case of large external hemorrhoids and/or persistent, symptomatic external hemorrhoids.




