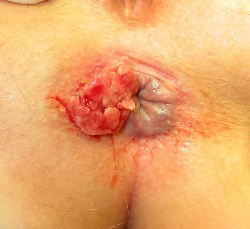
Bleeding from your rectum or anus is never a pleasant experience, and it can understandably cause immediate panic. Generally, bright red blood indicates bleeding in the lower rectum, while dark red blood indicates bleeding from deeper and further up in the body. While passing dark red blood is usually a sign of digestive bleeding and requires immediate attention, any amount of rectal bleeding should be taken seriously.
Bleeding from your rectum or anus is never a pleasant experience, and it can understandably cause immediate panic. Generally, bright red blood indicates bleeding in the lower rectum, while dark red blood indicates bleeding from deeper and further up in the body. While passing dark red blood is usually a sign of digestive bleeding and requires immediate attention, any amount of rectal bleeding should be taken seriously.
While rectal bleeding can be caused by pesky hemorrhoids, there are a number of other potential causes ranging from fistulas and fissures to more serious cases of colon/bowel cancer.
1. Anal Fistula
An anal fistula is an inflammatory tunnel under the skin connecting the anal canal and the surface of the surrounding skin. Most fistulas occur from an anorectal infection, where the anal crypts are infected and cysts containing pus form near the anal canal. Fistulas are often misdiagnosed as hemorrhoids, as symptoms can be similar, including drainage from the anus, itchiness and pain during bowel movements. They can be treated with antibiotics, pain meds and a fistulotomy.
2. Anal Fissure
An anal fissure is a small rip or tear in the lining of the anal cana typically caused by trauma to the inner lining of the anus via a bowel movement or stretching of the anal canal. They can be painful, but fissures often heal within a few weeks through increasing fiber/fluid intake to keep stool soft and help ease bowel movements.
3. Colon Cancer
As scary as it may sound, rectal bleeding is a dangerous sign of colon cancer and must be taken very seriously. Symptoms of colorectal cancer include abdominal pain, a change in bowel habits, an anal or rectal lump, and bleeding during bowel movements. Click here to read our post on the differences between rectal cancer and hemorrhoids.
4. Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, otherwise known as the stomach flu, is a common bacterial infection that causes diarrhea, fever and vomiting. Due to inflammation in the stomach and colon, the bowel becomes more sensitive during the illness and may cause bloody stools. While the process is uncomfortable, gastroenteritis normally clears up after a few days of rest and hydration.
5. Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis is a chronic bowel condition that causes small bulges or pockets to develop in the lining of the intestine/digestive tract. If these bulges become inflamed or infected, abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and bloody stools can occur. More common in people over 40, diverticulosis can be treated using diet modifications, antibiotics and, if needed, surgery.
6. Rectal Prolapse
Believe it or not, a bit of your intestine can actually slip outside of your body. A rectal prolapse occurs when part of the large intestine slips outside the anus, which can happen during a bowel movement. This in turn causes pain and bright red blood in the stool, as well as difficulty in controlling your bowel movements. A prolapse usually requires surgical treatment, so call your doctor right away.
7. Polyps
Polyps are non-cancerous growths that can develop along the lining of your bowel. They’re pretty common and don’t usually manifest symptoms. In more severe cases, they can cause diarrhea, constipation, mucus in the stool and bloody stools. While most polyps do not escalate into cancer, there is still risk of cancer development. Be sure to call your doctor for a full examination.
8. Internal Bleeding
As mentioned earlier, darker colored blood can be a sign of internal bleeding in your digestive system. It can also be a sign of cancer, stomach ulcers or severe gastrointestinal disease. If you see dark red blood in your stool call your doctor ASAP.
9. Colitis
Colitis is a chronic inflammation of the innermost lining of the large intestine and rectum. Small ulcers develop in the lining of the bowel, which then bleed and produce pus. This causes recurring diarrhea, abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and the frequent urge to pass stools. Management of colitis conditions can include antibiotics, medications and surgery.
10. Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI)
Sexually transmitted infections (STI) can result from unprotected anal sex and cause inflammation of the lining of the anus, which can lead to bleeding and pus. Treatment includes antibiotics and antiviral/antifungal medications.
 Because the symptoms of hemorrhoids and early-stage rectal/colon cancer are very similar, people often confuse and, at times, misdiagnose the two conditions. Since the treatment method for each condition is vastly different, it’s important to know how to differentiate hemorrhoids from rectal cancer and proceed with the appropriate treatment options.
Because the symptoms of hemorrhoids and early-stage rectal/colon cancer are very similar, people often confuse and, at times, misdiagnose the two conditions. Since the treatment method for each condition is vastly different, it’s important to know how to differentiate hemorrhoids from rectal cancer and proceed with the appropriate treatment options.